Each of us has four paired cavities (spaces) in our head that are connected to the nose by narrow channels. These cavities, known as sinuses, produce thin mucus that drains out of the channels of the nose. This drainage helps keep the nose clean and free of particles and bacteria.
Normally, sinuses are filled with air. But when sinuses become blocked and filled with fluid, bacteria can grow and cause an infection (bacterial sinusitis).
Conditions that cause sinus blockage include:
· the common cold
· allergic rhinitis (swelling of the lining of the nose due to allergies)
· nasal polyps (small growths in the lining of the nose), or
· a deviated septum (the wall between the left and right nostril is crooked).
Allergies, such as hay fever, can also cause swelling and poor drainage of the sinuses.
One confusing factor to consider is that many people with “sinus headaches†are actually suffering from migraines. In fact, in large clinical studies, up to 90% of people who reported sinus headaches were diagnosed with migraines instead. Migraines can cause headaches in combination with facial pressure over the sinuses, a runny nose, and nasal congestion. If you have symptoms that involve the sinuses, it may be difficult to tell if you have sinusitis, a cold, nasal allergy, or even a migraine. This article will describe the symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment of sinusitis, and how to tell the difference between sinusitis, cold, migraines, and nasal allergy.
What is sinusitis?
Sinusitis is an inflammation, or swelling, of the tissue lining the sinuses. There are two types of sinusitis:
·
Acute bacterial sinusitis: a sudden onset of cold symptoms such as runny nose, stuffy nose, and facial pain that does not go away after 10 days, or symptoms that seem to begin improving but return worse than the initial symptoms. It responds well to antibiotics and decongestants.
·
Chronic sinusitis: a condition defined by nasal congestion, drainage, facial pain/pressure, and decreased sense of smell for at least 12 weeks.
Who gets sinusitis?
Every year, approximately 1 billion Americans have at least one episode of viral sinusitis. About 37 million will develop a bacterial sinusitis. People who have the following conditions have a higher risk of sinusitis:
· Nasal mucus membrane swelling, as from a common cold or allergies
· Blockage of drainage ducts, leading to trapping of mucus
· Structure differences that narrow the drainage ducts
· Conditions that result in an increased risk of infection
· Polyps (growths)
In children, common factors in the environment that contribute to sinusitis include allergies, illness from other children at day care or school, and smoke in the environment.
In adults, the contributing factors are most frequently viral infections, allergies, and smoking.
What are the signs and symptoms of acute sinusitis?
The primary symptoms of acute sinusitis include:
· Facial pain/pressure/tenderness
· Nasal stuffiness
· Nasal discharge (thick yellow or green discharge from nose), especially if it is long-lasting
· Loss of smell and taste
· Cough/congestion
Additional symptoms may include:
· Fever of 102° or higher
· Ear pain
· Headache
· Bad breath
· Fatigue
· Ache in upper jaw and teeth
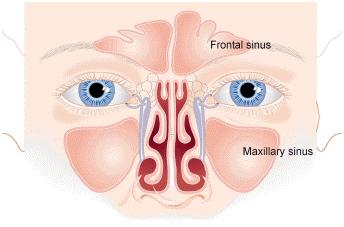
How is sinusitis diagnosed?
To diagnose sinusitis, your doctor will discuss your symptoms and examine your nose for swelling and drainage. Your personal history is most important in diagnosing sinusitis.
A physical exam of the ears, nose, and throat is performed to look for signs of obstruction (blockage) or infection. An endoscope (a small lighted/optical instrument) may be used to look inside the nose. In general, X-rays or CT scans do not play any role in the diagnosis of acute sinusitis.
Some patients may have conditions that may need to be referred to a specialist, such as an ear, nose, and throat (ENT) physician. Additional diagnostic tests may be needed. Tests for these more complicated cases may include cultures, allergy testing, CT scan of the sinuses, or nasal endoscopy. Nasal endoscopy allows doctors to look directly inside the nose to see sinus drainage pathways.
How is sinusitis treated?
Acute sinusitis. If you have a simple sinusitis infection, your health care provider may recommend treatment with decongestants like Sudafed and over-the-counter medications for cold and allergy, nasal saline irrigation, and drinking fluids (as most sinusitis is viral).
If symptoms do not improve after at least 10 days, if the symptoms seem to be getting worse, or if medications for cold or allergy do not improve symptoms, a bacterial infection may be causing the sinusitis. In this case, antibiotics are given for 7 days in adults and 10 days in children. Antibiotics should improve symptoms within 48 hours.
Oral or topical decongestants may be prescribed to relieve symptoms. Use of prescription intranasal steroid sprays might be added to help control symptoms. However, non-prescription drops or sprays should not be used beyond 5 days -- or they may actually increase congestion.
Chronic sinusitis. Treating chronic sinusitis begins with controlling the underlying condition, which is most often allergies. Standard treatments include intranasal steroid sprays, topical antihistamine sprays, or antihistamine pills, and leukotriene antagonists such as montelukast. Often you will be encouraged to rinse the nose with saline irrigations. Sometimes medications may be added to these irrigations.
If sinusitis is not controlled, the next step is a CT scan of the sinuses. This allows for a direct view of the nose and surrounding sinuses. Based upon CT findings, surgery may be recommended.
Will I need to make lifestyle changes?
If you have indoor allergies, avoiding triggers -- such as animal dander and dust mites – is recommended in addition to medications.
Smoking is never recommended, but if you do smoke, strongly consider a program to help you stop smoking, as this may be the main reason you have sinus infections. No special diet is required, but drinking extra fluids helps to thin nasal secretions.
What are the symptoms of the common cold?
An upper respiratory infection (the common cold) is usually caused by a virus that infects the nose and throat. Most upper respiratory infections are not bacterial and do not respond to antibiotics. A cold may cause swelling in the sinuses, preventing the outflow of mucus.
Cold symptoms include nasal congestion, runny nose, post-nasal drip (drop-by-drop release of nasal fluid into the back of the throat), headache, achiness, and fatigue. Cough and fever may also go along with these symptoms.
Cold symptoms usually build, peak, and slowly disappear. No treatment is necessary for a cold, but some medications can ease symptoms. For example, decongestants may decrease drainage and open the nasal passages. Analgesics (pain relievers) may help with fever and headache. Cough medication may help, as well. Colds will typically last from a few days to about a week.
What is the harm in getting an antibiotic for a common cold?
Viral infections like the common cold are not cured by antibiotics. Taking an antibiotic for a viral infection unnecessarily puts you at risk for side effects related to the antibiotic. In addition, the overuse of antibiotics leads to antibiotic resistance, which may make future infections more difficult to treat. Finally, the use of inappropriate medication increases health care costs unnecessarily.
What are the symptoms of nasal allergy?
Symptoms of nasal allergy include:
· Sneezing
· Itchy nose
· Clear, watery nasal discharge
· Nasal blockage
· Feeling fatigued
How is nasal allergy treated?
Usually medications are prescribed to relieve symptoms. These may include antihistamines, with or without decongestants, or steroid nasal sprays. Other nasal sprays, which deliver antihistamines or cromolyn sodium, are sometimes helpful. If allergy symptoms are chronic (long-term), allergy testing and allergy shots (immunotherapy) may be helpful.
How can I tell if I have a sinus infection, cold, or nasal allergy?
Although the symptoms of sinusitis and nasal allergy may occur with a common cold, in general, cold-related symptoms disappear within 1 week.
The point at which a normal cold ends and a sinus condition begins is not always easy to know. If you are fighting off a cold and develop symptoms of a sinus infection or nasal allergy, see your health care provider. You will be asked to describe your symptoms and medical history.
 
How do I know if my sinus condition requires the care of an ear, nose, and throat specialist?
Most routine sinus conditions are easily cared for by primary care physicians. If, however, you are bothered by ongoing abnormal symptoms, recurring infections, or have abnormal X-ray findings or complications, a referral to a specialist is appropriate.




